Executive Summary
In the rapidly evolving healthcare landscape, efficient and effective testing of information technology (IT) systems is crucial. e4health’s Testing Office model represents a best-in-class approach to healthcare IT testing, combining LEAN engineering principles with deep industry expertise.
Key highlights of the e4health Testing Office:
- Reduces testing costs by up to 30% compared to traditional in-house methods
- Improves testing quality, with defect detection rates 25% higher than industry averages
- Accelerates go-live timelines by an average of 20%
- Enhances stakeholder confidence through transparent, data-driven processes
This whitepaper outlines how e4health’s Testing Office model addresses the unique challenges of healthcare IT testing, providing a scalable, efficient, and reliable solution for health systems of all sizes. By leveraging LEAN principles and industry-specific knowledge, e4health’s approach not only optimizes testing processes but also contributes to improved patient care outcomes and operational efficiency.
Introduction
Healthcare IT systems are intricate, interconnected, and critical to patient care and organizational operations. The complexity of these systems, combined with stringent regulatory requirements and the high stakes of patient safety, makes comprehensive testing an absolute necessity. As healthcare organizations continue to adopt new technologies and integrate existing systems, the importance of robust testing methodologies cannot be overstated.
This whitepaper explores:
- The challenges faced in healthcare IT testing
- e4health’s innovative Testing Office model
- How LEAN engineering principles are applied to testing processes
- The benefits and outcomes of implementing a Testing Office
By delving into these areas, we aim to provide healthcare leaders and IT professionals with a comprehensive understanding of how e4health’s Testing Office can transform their approach to system testing, ultimately leading to improved patient care, reduced costs, and enhanced operational efficiency.

Challenges in Healthcare IT Testing
lthcare organizations face numerous obstacles in effectively testing their IT systems. These challenges are multifaceted and often interconnected, requiring a holistic approach to overcome:
- Complexity: Multiple interconnected systems, workflows, and stakeholders create a vast testing scope. Healthcare IT ecosystems typically include electronic health records (EHRs), laboratory information systems, pharmacy management systems, and various specialty applications. Each of these systems must not only function independently but also integrate seamlessly with others, creating a complex web of interactions that must be thoroughly tested.
- Resource Constraints: Limited availability of skilled testing personnel and subject matter experts is a common issue. Healthcare organizations often struggle to maintain a dedicated testing team with the necessary expertise across all systems and clinical workflows. This shortage can lead to incomplete testing or overreliance on vendors for critical testing activities.
- Time Pressure: Tight project timelines often lead to rushed or incomplete testing. The pressure to implement new systems or updates quickly, often driven by regulatory requirements or operational needs, can result in compromised testing processes. This rush can lead to undetected issues that may impact patient care or operational efficiency post-implementation.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring adherence to HIPAA, HITECH, and other healthcare-specific regulations is paramount. Testing must not only verify system functionality but also confirm that patient data privacy and security measures are robust and compliant with all applicable laws and standards.
- Data Integrity: Maintaining accuracy and consistency of patient data across systems is critical. Testing must verify that patient information is accurately captured, stored, and transmitted between different systems without loss or corruption. This includes ensuring that data mappings between systems are correct and that data transformations maintain the original meaning and context of the information.
- Integration Testing: Verifying seamless communication between diverse healthcare applications is complex. With the increasing adoption of interoperability standards like HL7 FHIR, testing must ensure that systems can exchange data accurately and efficiently, maintaining the integrity and context of the information across different platforms and vendors.
- User Acceptance: Engaging clinicians and staff in meaningful testing scenarios can be challenging. Healthcare professionals are often time-constrained, making it difficult to involve them in comprehensive testing processes. However, their input is crucial for ensuring that systems meet real-world clinical needs and workflows.
- Cost Management: Balancing comprehensive testing with budget constraints is an ongoing challenge. Healthcare organizations must weigh the costs of thorough testing against the potential risks and costs associated with system failures or inefficiencies post-implementation.
e4health’s Testing Office model directly addresses these challenges through a structured, efficient, and scalable approach. By leveraging LEAN principles and healthcare-specific expertise, e4health provides a comprehensive solution that optimizes testing processes while ensuring high-quality outcomes.
The e4health Testing Office Solution
The e4health Testing Office is a comprehensive model that combines people, processes, and technology to optimize healthcare IT testing. This innovative approach is designed to address the unique challenges of healthcare IT environments while maximizing efficiency and effectiveness. Key components include:
- LEAN Engineering: Applying principles of waste reduction and continuous improvement to testing processes. This involves identifying and eliminating non-value-added activities, streamlining workflows, and fostering a culture of ongoing optimization. For example, e4health’s Testing Office might implement standardized test case templates to reduce redundancy and improve consistency across different testing phases.
- Standardized Methodologies: Consistent, repeatable testing approaches across projects and systems. e4health has developed a set of best practices and methodologies tailored to healthcare IT testing, ensuring that all testing activities follow a proven, efficient process. This standardization helps reduce variability and improves the overall quality of testing outcomes.
- Skilled Resource Pool: Access to experienced healthcare IT testers and subject matter experts. e4health maintains a team of professionals with deep knowledge of healthcare systems, workflows, and regulatory requirements. This expertise allows for more effective test planning, execution, and issue resolution.
- Automated Tools: Leveraging technology to increase efficiency and coverage of testing efforts. e4health employs a suite of automated testing tools specifically configured for healthcare IT environments. These tools can perform repetitive tests quickly and accurately, freeing up human testers to focus on more complex scenarios that require clinical judgment.
- Knowledge Management: Centralized repository of testing artifacts, scenarios, and best practices. This repository serves as a valuable resource for current and future testing efforts, promoting knowledge sharing and continuous improvement across the organization.
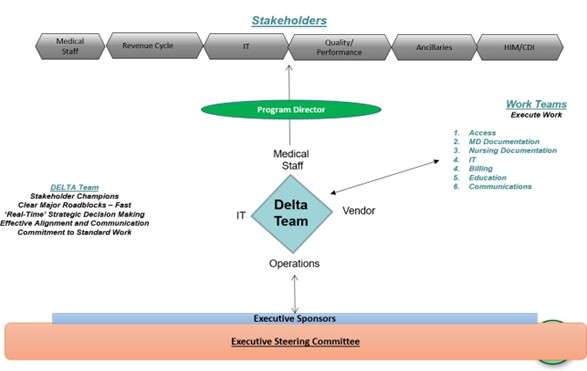
The Importance of Testing Governance
The Testing Office operates under a clear governance structure designed to ensure objectivity, stakeholder alignment, and effective risk management:
- Independence: Maintains objectivity by reporting directly to executive leadership. This structure ensures that testing activities are not unduly influenced by project timelines or departmental pressures, allowing for unbiased assessment of system readiness.
- Stakeholder Representation: Includes voices from IT, clinical, and operational teams. A diverse governance board ensures that testing priorities and strategies align with the needs of all key stakeholders within the healthcare organization.
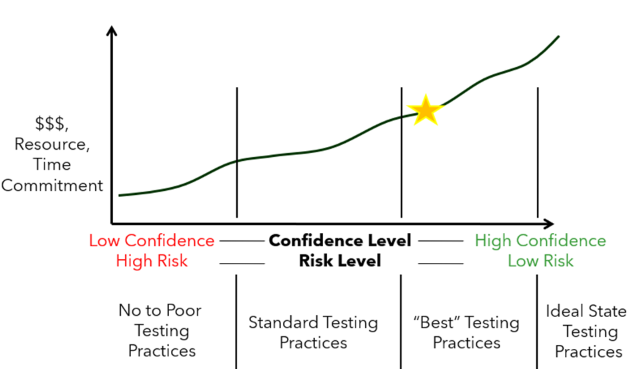
- Risk Management: Utilizes a “Cost Confidence Curve” to balance testing depth with resource allocation. This innovative approach helps organizations make informed decisions about where to focus testing efforts based on potential impact and resource constraints.
The Testing Cost-Confidence Curve: The definition of “acceptable levels of testing” is based on the combination of a customer’s requirements for Confidence Levels against their willingness to invest resources and cost.
Planning and Execution
The Testing Office employs a structured approach to planning and executing testing initiatives, ensuring comprehensive coverage and efficient use of resources:
- Scope Definition: Clearly outlining testing boundaries and objectives. This involves collaborating with stakeholders to identify critical systems, workflows, and integration points that require testing. The scope definition process helps prioritize testing efforts and ensures alignment with organizational goals.
- Test Strategy Development: Creating a comprehensive roadmap for testing activities. The strategy outlines the types of tests to be performed (e.g., functional, integration, performance), testing environments, data requirements, and resource allocation. This strategic approach ensures that all aspects of the system are adequately covered.
- Resource Allocation: Assigning skilled personnel to specific testing tasks. e4health’s Testing Office matches the expertise of its testing professionals with the requirements of each testing phase, ensuring that the right skills are applied to each task.
- Test Case Design: Developing detailed scenarios that cover critical workflows. Test cases are designed to simulate real-world usage patterns and edge cases, ensuring thorough coverage of system functionality and potential failure points.
- Execution and Monitoring: Conducting tests and tracking progress in real-time. The Testing Office uses advanced monitoring tools to provide visibility into testing progress, allowing for quick identification and resolution of bottlenecks or issues.
- Defect Management: Systematic approach to identifying, prioritizing, and resolving issues. e4health employs a robust defect tracking system that categorizes issues based on severity and impact, ensuring that critical problems are addressed promptly.
- Reporting and Analytics: Providing stakeholders with clear, actionable insights. Regular reports and dashboards offer a comprehensive view of testing progress, defect trends, and overall system readiness, enabling informed decision-making throughout the testing process.
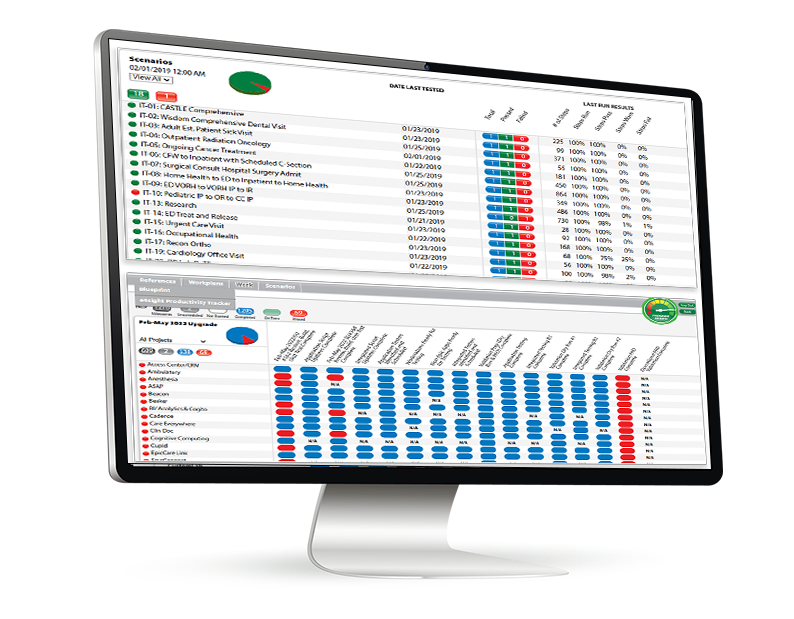
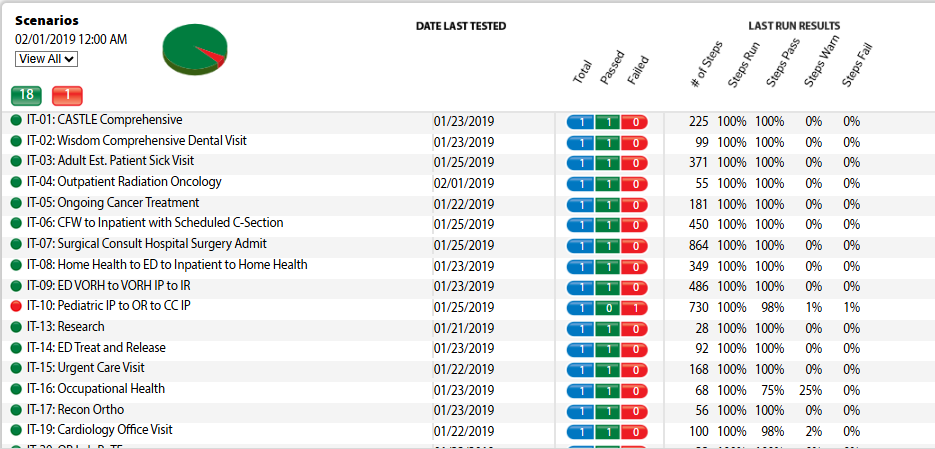
Transparency and Results
The e4health Testing Office prioritizes transparency and measurable outcomes, ensuring that stakeholders have full visibility into the testing process and its results:
- Real-time Dashboards: Stakeholders can access up-to-date testing progress and results. These dashboards provide a visual representation of key metrics such as test case execution rates, defect discovery trends, and overall project status. This real-time visibility allows for quick decision-making and resource adjustments as needed.
- Comprehensive Reporting: Detailed analysis of test coverage, defect trends, and risk areas. e4health’s reporting goes beyond simple pass/fail metrics to provide insights into system quality, potential vulnerabilities, and areas for improvement. These reports help organizations understand the true state of their systems and make informed decisions about go-live readiness.
- Metrics-driven Approach: Quantifiable measures of testing efficiency and effectiveness. The Testing Office tracks and analyzes a range of metrics, including defect detection rates, test case execution efficiency, and time-to-resolution for identified issues. These metrics not only demonstrate the value of the testing process but also guide continuous improvement efforts.
- Continuous Improvement: Regular retrospectives to refine and enhance testing processes. After each major testing phase or project, the Testing Office conducts thorough reviews to identify lessons learned and opportunities for optimization. This commitment to continuous improvement ensures that the testing process becomes more efficient and effective over time.
In Conclusion
The e4health Testing Office model represents a paradigm shift in healthcare IT testing. By combining LEAN principles, healthcare expertise, and innovative tools, e4health delivers:
- Higher quality testing with fewer resources, achieved through standardized processes and automation
- Accelerated project timelines without compromising thoroughness, enabled by efficient resource allocation and streamlined workflows
- Increased stakeholder confidence in IT system reliability, supported by transparent reporting and comprehensive test coverage
- Measurable cost savings and efficiency gains, demonstrated through quantifiable metrics and continuous improvement
For healthcare organizations seeking to optimize their IT testing processes, the e4health Testing Office offers a proven, scalable solution that drives better outcomes for both patients and providers. By addressing the unique challenges of healthcare IT testing and leveraging industry-specific expertise, e4health empowers organizations to implement and maintain robust, reliable systems that support high-quality patient care and efficient operations.
Trademarks
e4health Testing Office, e4caster, e4health LEAN Engineering, e4health LEAN Blueprint, e4health DELTA Team, and LEAN Governance are registered trademarks of e4health. All other trademarks or registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Contact Information
For more information about e4health’s Testing Office and other healthcare IT solutions, please visit www.e4health.com/testing or contact info@e4.health.