Definition:
HIV Disease is caused by human immunodeficiency virus, of all types, with destruction of CD4+ T-lymphocytes that help mediate the body’s immune response to infection.
· The virus is bloodborne
· It is most often transmitted through:
o Sexual intercourse
o Shared IV drug needles
o Mother-to-child transmission during birth or breastfeeding
Diagnostic Criteria:
The CDC is responsible for establishing the definitive case definitions of HIV infection and HIV disease (AIDS).
- HIV infection (HIV + without AIDS)- Identified through two different HIV antibody or antigen/antibody tests or by non-antibody virologic testing. This describes a person with a + HIV test but does meet the criteria for HIV disease (AIDS).
· HIV disease/AIDS- An HIV + patient with a past or present occurrence of one of the following:
o Absolute CD4+ T-lymphocyte count< 200 or
o An AIDS defining condition
· CDC AIDS-defining conditions:
o Pneumocystis pneumonia
o Certain lymphomas
o Systemic candidiasis
o Kaposi’s sarcoma
o Other unusual bacterial, fungal, parasitic, viral infections
· The complete list of AIDS defining conditions can be found at www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/rr5710a2.htm.
· The stages of HIV are defined by the CD4 count (cells /uL):
o Early (CD4 > 500)
o Intermediate (CD4 200-500)
o Advanced (CD4 100-200)
o Late stage (CD4 < 100)
Coding Considerations:
- HIV disease/AIDS (B20)- If B20 has ever been diagnosed and coded, then it will always be coded on subsequent encounters.
- HIV + (Z21)-Used when the patient has never been diagnosed with AIDS or AIDS-defining diagnosis.
- Only confirmed cases of HIV are coded, not suspected or probable.
- In this context, “confirmation” does not require documentation of positive serology or culture for HIV; the provider’s diagnostic statement that the patient is HIV positive or has an HIV-related illness is sufficient.
- Sequencing of HIV codes
- If a patient is admitted for an HIV-related condition, the principal diagnosis should be B20 followed by additional diagnosis codes for all reported HIV-related conditions.
- Exceptions:
- Hemolytic-uremic syndrome associated with HIV disease
- HIV in pregnancy: If a patient is admitted because of an HIV-related illness, assign O98.7-, Human immunodeficiency [HIV] disease complicating childbirth and the puerperium, followed by B20 and the code(s) for the HIV-related illness(es). Codes from Chapter 15 always take sequencing priority.
- If a patient with a history of HIV disease is currently managed on antiretrovirals, assign code B20.
- Review the following Coding Clinics:
- AHA Coding Clinic, First Quarter 2022, p. 36
- AHA Coding Clinic, First Quarter 2022, p. 27
- AHA Coding Clinic, First Quarter 2021, p. 52
- AHA Coding Clinic, Fourth Quarter 2020, p. 97
- AHA Coding Clinic, Second Quarter 2020, p. 23
- AHA Coding Clinic, First Quarter 2019, p. 8
- Exceptions:
- If a patient is admitted for an HIV-related condition, the principal diagnosis should be B20 followed by additional diagnosis codes for all reported HIV-related conditions.
CDI Practice Considerations:
- The CDC recommends using the term HIV disease to describe AIDS.
- The term HIV infection describes an HIV+ person who does not meet criteria for HIV disease.
- If the provider has documented HIV, HIV+, or HIV infection, but prior records show the code B20, a query may be necessary for clarification.
- B20 provides a CC as a secondary diagnosis and both B20 and Z21 will influence risk adjustment.
- When HIV is assigned as EITHER the PDx or as a SDx, with a “major related” condition, an HIV DRG will be assigned.
- HIV DRGs:
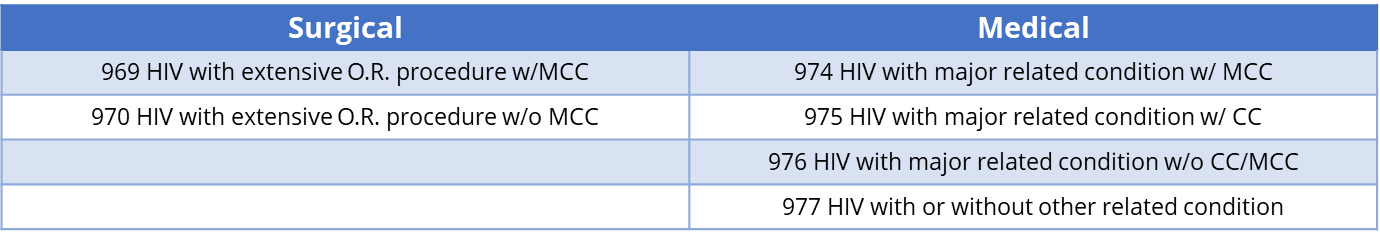
- HIV “major related” conditions: Pneumonia, Encephalopathy, Sepsis, Endocarditis, Lymphoma, Histoplasmosis, Oral thrush, Cryptococcus, Cytomegalovirus, Toxoplasmosis, Myelitis, Herpes viral infections, Organic mental disorders, Psychosis, Salmonella infections, etc.
- If a patient is admitted and treated for a condition that is not on the “major related” condition list, the PDx is the unrelated condition and HIV is secondary.
- Example: Pt with HIV disease falls and is admitted for hip fracture and ORIF, the PDx is hip fracture and B20 is a CC.
- CDI reviews should consider the CD4 count when reviewing for the presence of possible infections or complications.
- A provider must link or unlink the HIV to the admission diagnosis. When documentation is unclear, a query should be placed.

Looking for CDI help?
Learn more about e4health CDI Solutions. Our Team is leading the way in the CDI industry.
e4health CDI Education
Need help to earn CEUs or education your team? Visit the IQ Education Center and get your free account or contact us for more information.
e4health is dedicated to elevating the business of healthcare. We are committed to offering support and the most current information and updates to collaborate with coding and CDI professionals to realize their fullest potential. We enthusiastically seek opportunities to develop ourselves and each other. We understand that knowledge is the key to success for our clients navigating the ever-changing health information management landscape.
Earn FREE ACDIS CEUs when you join Staci Josten, RN, BSN, CCDS, Alyson Swinehart, BSN, RN, CCDS, and other CDI leaders for a roundtable discussion regarding important, timely industry topics! The topic for February’s discussion is CDI Compliance 360: Auditing for CDI Quality and Accuracy. We will provide background on this topic, share industry insights, and facilitate collaborative discussion with guided questions and answers.

The information and opinions presented here are based on the experience, training, and interpretation of e4health. Although the information has been researched and reviewed for accuracy, e4health does not accept any responsibility or liability regarding errors, omissions, misuse, or misinterpretation. This information is intended as a guide; it should not be considered a legal/consulting opinion or advice.